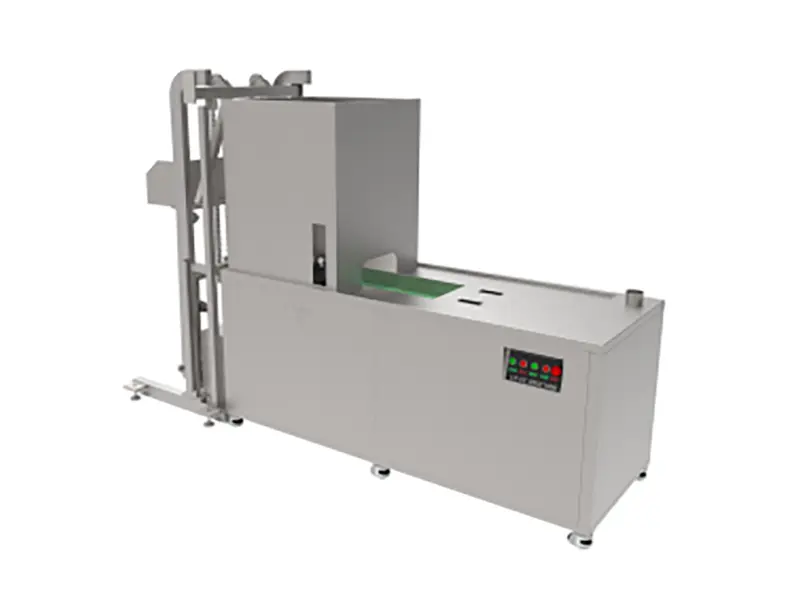
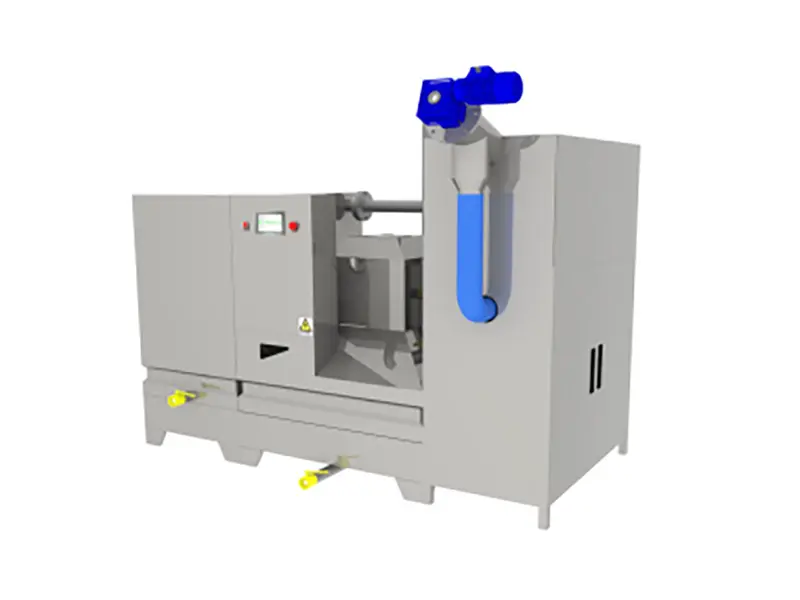
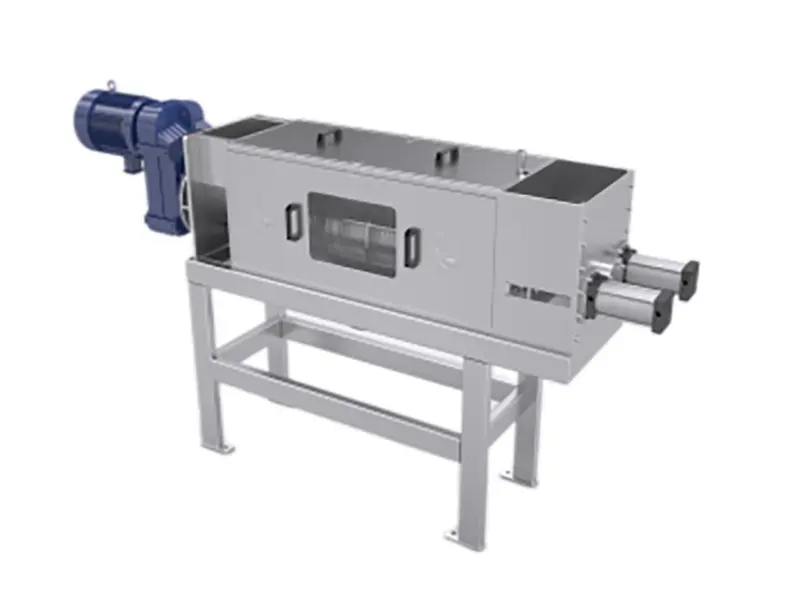
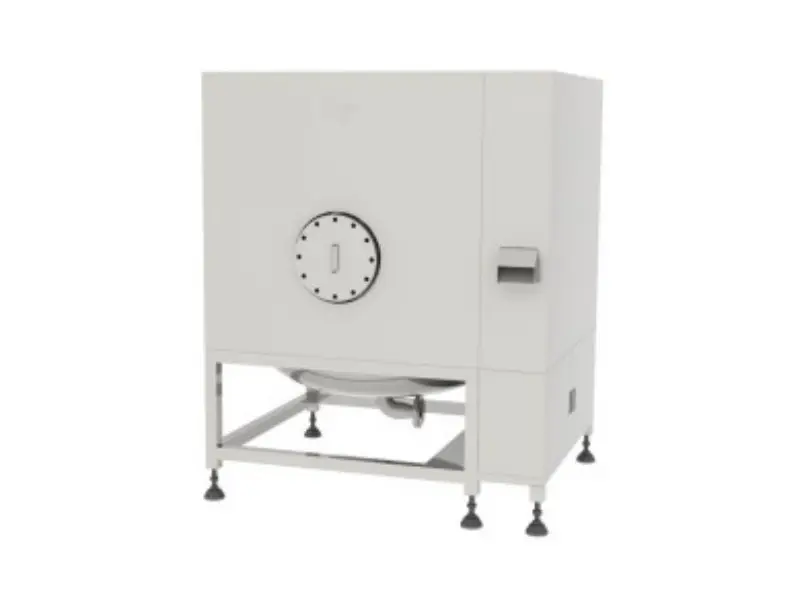
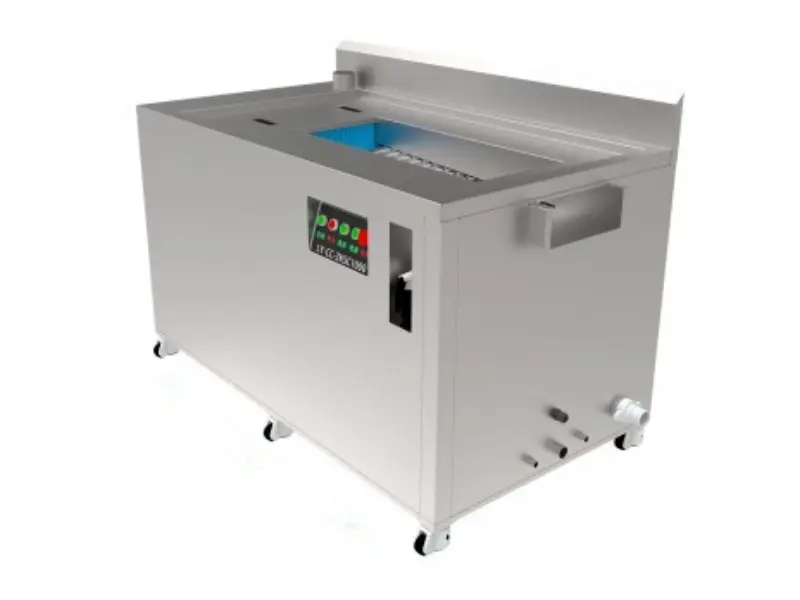
Waste Lithium Battery Recycling


Features
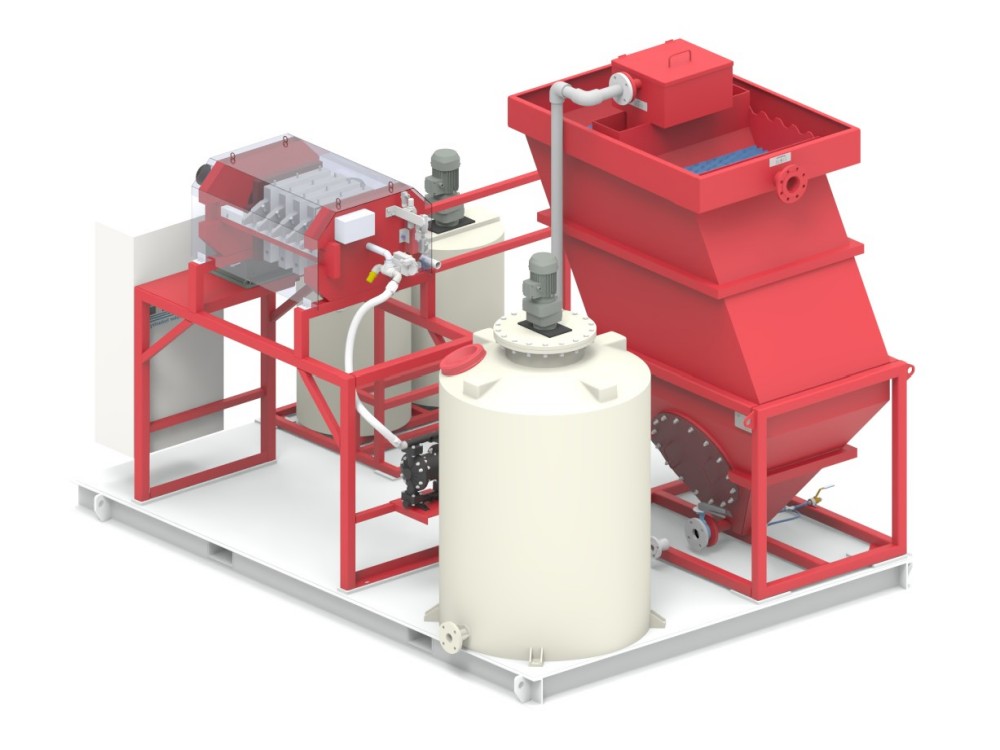
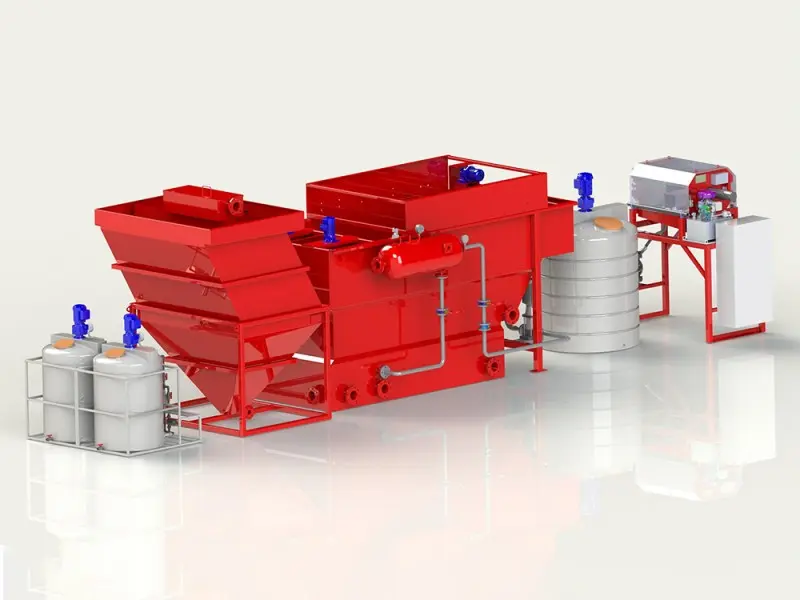
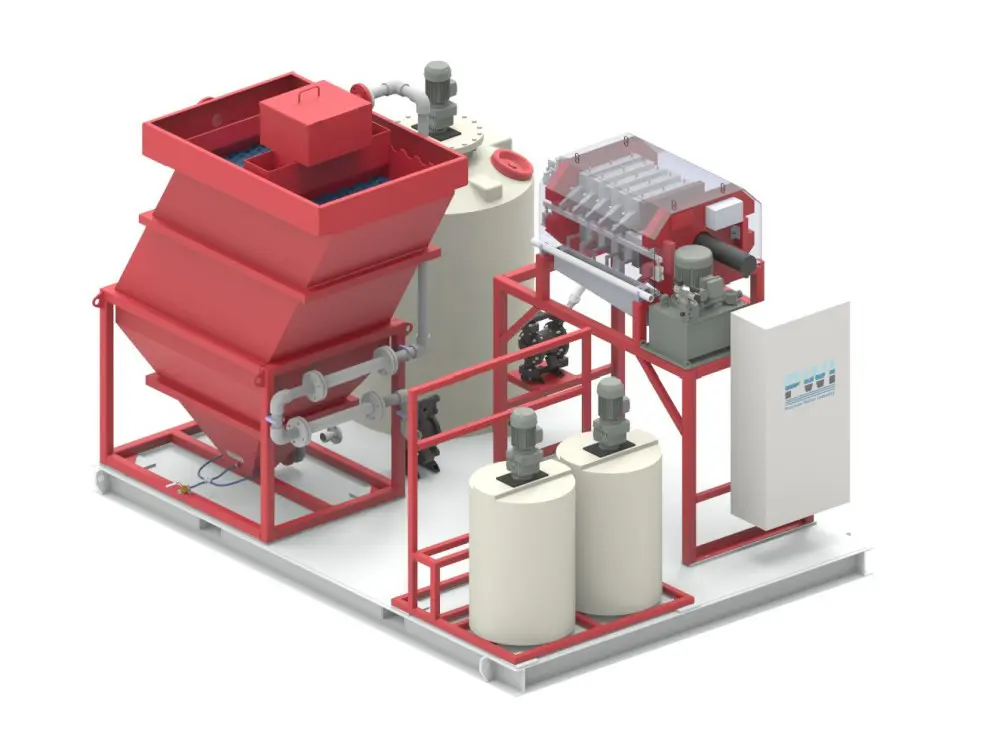
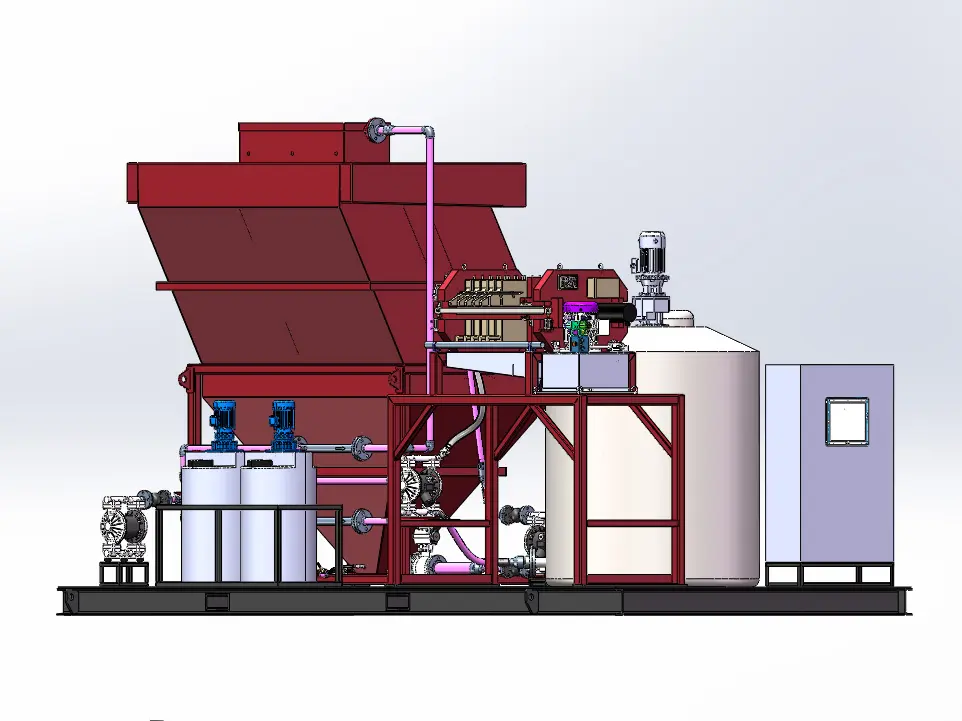
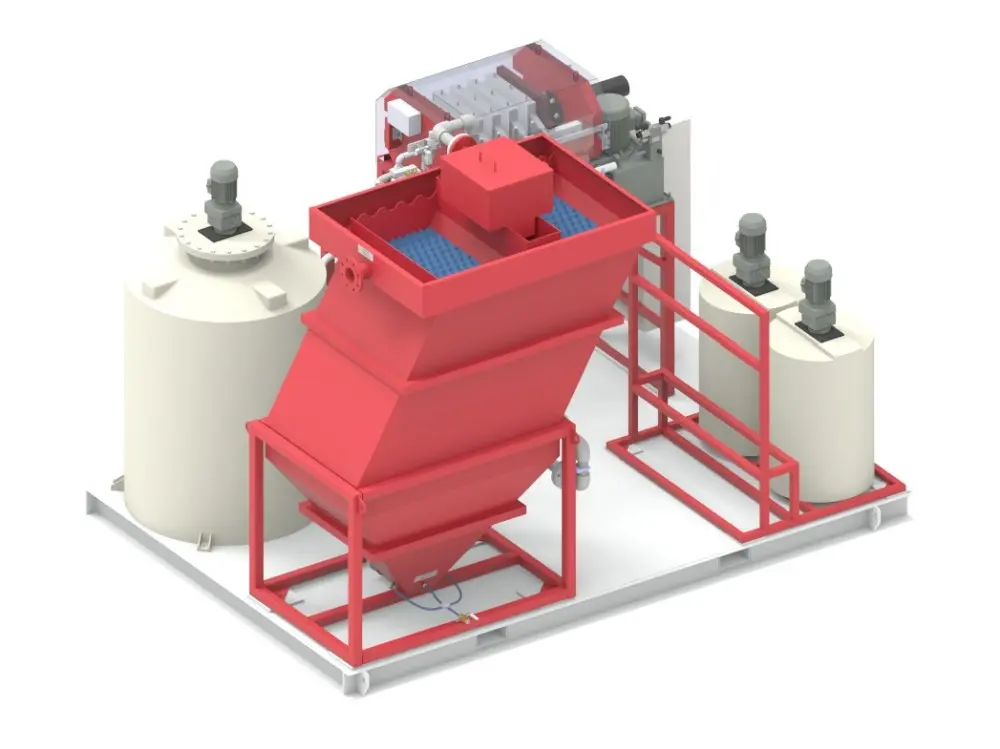
In the process of recycling waste lithium batteries or purifying and reusing black powder, there are high temperatures, strong acids, strong alkalis and highly oxidizing environments, which require multiple stirring reactions and filtrations, and the emission of toxic gases needs to be considered.
Process flow chart
Please understand that this is not open to the public yet. If you need to communicate, please contact our technical staff.
Configuration Table
Please understand that this is not open to the public yet. If you need to communicate, please contact our technical staff.
Feature Comparison
Please understand that this is not open to the public yet. If you need to communicate, please contact our technical staff.
Optional functions
Please understand that this is not open to the public yet. If you need to communicate, please contact our technical staff.
Product Introduction
In the intricate process of recycling waste lithium batteries or purifying and reusing black powder, a series of formidable challenges emerge due to the harsh operational conditions involved. The recycling and purification procedures are characterized by the presence of extreme environments, including high - temperature settings that can reach several hundred degrees Celsius. These elevated temperatures are necessary to break down the complex chemical compounds within the waste materials, facilitating the extraction of valuable metals and the separation of components.
Moreover, the process often entails exposure to strong acids and alkalis. Strong acids, such as sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, are employed to dissolve metal oxides and other substances, while strong alkalis like sodium hydroxide are used for various chemical reactions and precipitation processes. Additionally, highly oxidizing environments are created to promote specific chemical transformations, which are crucial for the efficient recovery of materials.
These operations demand multiple stirring reactions to ensure uniform mixing and thorough chemical interactions, as well as numerous filtration steps to separate solids from liquids and purify the resultant solutions. Each stirring reaction must be precisely controlled to optimize the reaction rate and product quality, while the filtration processes require high - performance equipment to handle the corrosive and abrasive nature of the materials.
Furthermore, an equally significant concern is the emission of toxic gases. During the recycling and purification processes, hazardous substances such as hydrogen fluoride, sulfur dioxide, and various volatile organic compounds may be released. These toxic gases pose serious threats to human health and the environment if not properly managed. Therefore, comprehensive gas treatment systems are essential to capture, neutralize, and safely discharge these gases, adding another layer of complexity to the already challenging recycling and purification operations.