The Wastewater Treatment Industry plays a crucial role in achieving sustainability. With over 80% of the world’s wastewater being discharged without treatment, this industry is vital. Untreated wastewater contaminates water bodies and endangers aquatic life. According to the United Nations, clean water is essential for health, food security, and ecosystem preservation.
The industry is not just about cleaning water; it is about resource recovery. Advanced treatment technologies can recover nutrients and energy from wastewater. The Global Water Intelligence reports that, by 2025, the market for recovered resources could exceed $1 trillion annually. This potential makes wastewater treatment a lucrative investment opportunities.
However, there are challenges. Many treatment facilities struggle with aging infrastructure and lack of funding. The need for innovation in wastewater management becomes evident. Addressing these issues can lead to sustainable practices and a healthier planet. The Wastewater Treatment Industry must embrace change to secure a better future for all.
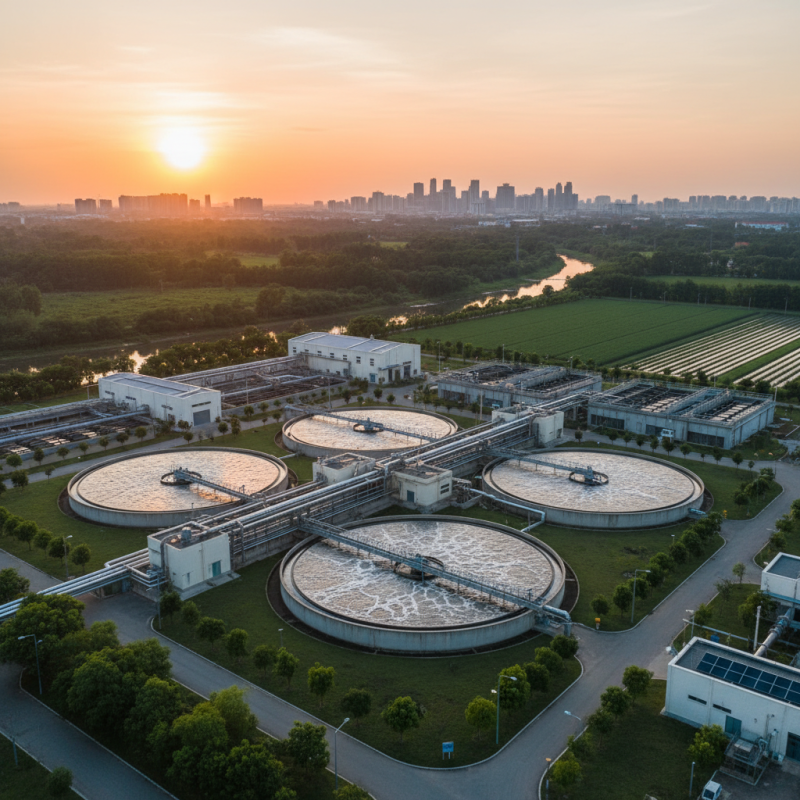

Wastewater treatment plays a critical role in effective water resource management. In 2021, it was estimated that around 80% of all wastewater globally is discharged without adequate treatment. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for improved infrastructure. Efficient treatment facilities recycle water, reducing the demand for fresh water sources. They help replenish groundwater supplies and maintain healthy ecosystems.
In regions facing severe water scarcity, treated wastewater can serve as a vital resource. According to recent reports, reusing treated wastewater could meet up to 30% of urban water demands. This reuse is particularly important as populations grow and climate change intensifies. However, only a fraction of municipalities currently utilize this option. Many still rely heavily on traditional water sources, which is unsustainable.
Despite advancements in technology, the treatment industry faces challenges. Operational costs can be high, limiting accessibility for smaller communities. Additionally, public perception often leans toward mistrust of reused water. Educating communities about the safety and benefits of treated wastewater is essential for broader acceptance. This step is crucial to overcoming resistance and fostering sustainable practices across all sectors.
Wastewater treatment plays a crucial role in environmental sustainability. It reduces harmful pollutants entering ecosystems. Clean water supports biodiversity and human health. Effective treatment processes help to recycle water. This process can alleviate water scarcity in many regions. Moreover, treated wastewater can be reused for agricultural purposes. This practice reduces the need for freshwater sources, an increasingly pressing issue.
Implementing advanced technologies in treatment facilities enhances efficiency. Sensors and automated systems can monitor water quality continuously. This provides timely data for better decision-making. Regular maintenance is vital. Neglecting treatment plants can result in chemical leaks. These leaks can damage local ecosystems. It’s essential to conduct routine checks for operational safety.
Tips: Educate your community on the importance of wastewater treatment. Hosting workshops can raise awareness. Encourage local businesses to adopt sustainable practices. Simple actions like reducing water waste can have a big impact. Every drop counts in the fight for sustainable water resources.

The wastewater treatment industry plays a vital role in our economy. This sector creates jobs and generates revenue. Treatment facilities require skilled workers to operate and maintain various systems. This employment boost is significant, especially in rural areas. There are also indirect jobs created in waste collection and environmental management. Many people depend on these jobs.
Investing in wastewater treatment has long-term economic benefits. Clean water supports agriculture, tourism, and health. Contaminated water has costly consequences. Illness and pollution can burden healthcare systems. Proper wastewater treatment reduces these risks, enhancing community well-being. However, challenges persist. Many facilities face aging infrastructure and limited funding. Upgrades often require substantial investment. Without adequate resources, the system struggles.
Communities must prioritize sustainable practices. Educating the public about water conservation can help. Many citizens remain unaware of how their actions impact water quality. Emphasizing responsible waste disposal can minimize contamination. Engaging communities fosters a collective effort to protect resources. Rainwater harvesting and recycling initiatives also demonstrate potential savings. This creates a dialogue for improvement and awareness.
The wastewater treatment industry plays a critical role in promoting sustainability. Recent innovations have redefined how we handle wastewater. Advanced filtration methods are now common. These technologies enable the recovery of clean water from polluted sources. Additionally, biologically-based systems are gaining traction. They utilize naturally occurring bacteria to break down contaminants effectively.
New approaches, like membrane bioreactors, are changing the landscape. These systems combine biological processes with membrane filtration. They achieve higher efficiency compared to traditional methods. However, challenges remain in implementation. High energy consumption and maintenance costs can deter users. These factors raise questions about scalability and accessibility for smaller communities.
Furthermore, there is a push for resource recovery from wastewater. Nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus can be extracted and reused. This not only decreases pollution but also serves agricultural needs. Yet, the technology is still evolving. The balance between innovation and practicality requires further exploration. We must consider economic and social implications too. Addressing these issues will be essential for creating a sustainable future in wastewater management.
Wastewater treatment plays a crucial role in achieving sustainability. However, the industry faces significant challenges. According to a report by the United Nations, over 80% of wastewater worldwide is released into the environment without treatment. This leads to severe pollution and health issues. A substantial portion of this unprocessed wastewater comes from urban areas, where population growth puts immense pressure on treatment facilities.
One major challenge is aging infrastructure. Many treatment plants were built decades ago and require upgrades. The World Economic Forum highlights that up to $1 trillion will be needed to modernize facilities globally by 2030. Investments are essential to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Technologies like membrane bioreactors and energy recovery systems can make a difference but require funding and research.
Another obstacle is public awareness. Many communities do not understand the importance of proper wastewater management. Education can drive change, helping to foster support for necessary regulations and financial backing. Local initiatives may struggle, lacking resources and technical expertise. Overcoming these barriers is crucial to building a sustainable wastewater treatment industry, yet the path forward remains fraught with complexities.
| Dimension | Current Status | Challenges | Future Directions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Technologies | Advanced treatment methods like membrane filtration. | High operational costs and energy consumption. | Development of energy-efficient technologies. |
| Regulatory Framework | Stringent regulations improving effluent standards. | Compliance costs and adapting to new regulations. | Harmonization of international standards. |
| Wastewater Reuse | Growing interest in potable and non-potable reuse. | Public perception and safety concerns. | Awareness campaigns and rigorous testing protocols. |
| Emerging Contaminants | Increased detection of pharmaceuticals and personal care products. | Lack of effective removal methods in existing systems. | Research on advanced treatment solutions. |
| Sustainability Practices | Incorporation of circular economy principles. | Integration challenges with existing infrastructure. | Investment in retrofitting and innovative designs. |






