The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) plays a vital role in shaping China's economic landscape. This agency is pivotal in implementing policies that affect various sectors, including infrastructure and energy. According to the China National Development and Reform Commission’s recent data, investments in renewable energy exceeded 500 billion Yuan in 2021, showcasing the agency's commitment to sustainable growth.
However, the NDRC also faces challenges. While it aims for balanced regional development, disparities in economic growth persist across provinces. Reports indicate that the gap between coastal and inland regions remains significant, prompting ongoing debates about the effectiveness of current policies. Stakeholders often question whether the NDRC's measures adequately address these inequalities.
In-depth analysis reveals that the NDRC is crucial for national strategy but requires continuous improvement. Its responses to the evolving global landscape are essential. As China strives for innovation and sustainability, the NDRC must evolve alongside these challenges, ensuring that development is not only rapid but also equitable.

The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) plays a crucial role in China's economic development. Established in 2003, it oversees macroeconomic planning and policy formulation. The NDRC is heavily involved in investment and resource allocation. According to a recent report, it managed over $500 billion in investments in 2022 alone, shaping key industries.
Managing economic structure adjustments is one of the NDRC's primary tasks. It aims to balance growth and sustainability. The NDRC also drafts long-term development plans. These plans address a wide range of sectors, from energy to urban planning. Experts report that the NDRC's influence is evident in the Green Development Initiative, which focuses on ecological sustainability.
Tips for understanding the NDRC's role: Keep track of its policies. They often affect various sectors directly. Look out for announcements regarding infrastructure projects. These can signal shifts in regional economic priorities. Engage with reports from reputable sources for precise data, as they can illuminate future trends. Remember, while the NDRC shapes policy, real-world outcomes can vary. Staying informed requires continual observation of its initiatives and their impacts.
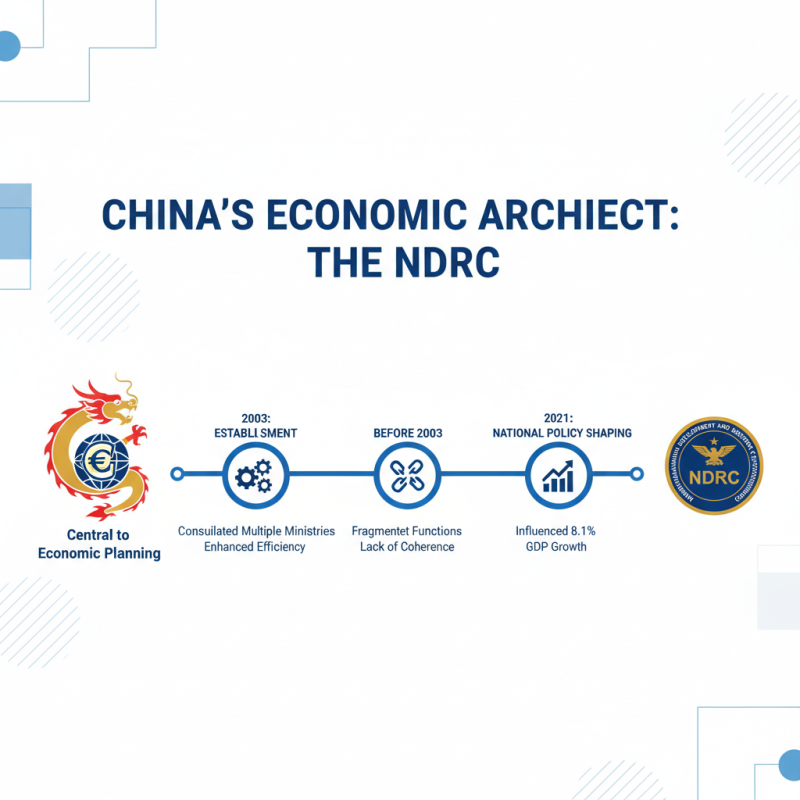
The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) is pivotal in China's economic planning. Established in 2003, it consolidated multiple ministries. Before its formation, the functions were fragmented and lacked coherence. This restructuring aimed to enhance efficiency in economic management. By 2021, the NDRC was instrumental in shaping national policies, influencing a GDP growth of 8.1% that year.
Throughout its history, the NDRC has faced challenges. Coordination among various governmental bodies has often been a struggle. Reports indicate bureaucratic inertia sometimes hinders quick decision-making. Additionally, balancing regional interests and national goals presents ongoing issues. An effective integration of these aspects is crucial for unlocking potential growth.
Despite these challenges, the NDRC has successes worth noting. For instance, its focus on sustainable development has led to a 20% reduction in carbon intensity since 2016. This reflects a commitment to both economic and environmental goals. Yet, critics argue that more should be done to address systemic inefficiencies. Overall, the NDRC remains a key player in navigating China's development landscape.
The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) plays a vital role in China’s economic planning. Its key responsibilities include formulating policies for economic and social development. This ensures that national priorities align with various sectors. The NDRC oversees crucial areas such as energy, transportation, and telecommunications. Each sector has unique challenges and opportunities.
One primary function of the NDRC is the regulation of investment. This involves assessing large projects to determine their viability. Often, the NDRC balances growth with environmental concerns. For instance, while developing infrastructure, it must also consider ecological impacts. This balance is not always achieved, leading to conflicts.
Another significant duty is monitoring prices. The NDRC examines the cost of essential goods and services. Sometimes, this regulation can lead to unintended consequences. For example, capping prices may create shortages. These complexities illustrate the delicate nature of economic management. The NDRC's tasks are crucial but fraught with challenges that require ongoing reflection and adjustment.
| Fact | Description |
|---|---|
| Established Year | The NDRC was established in 2003. |
| Main Role | It acts as the macro-economic management agency of the Chinese government. |
| Policy Formulation | Formulates national economic and social development strategies. |
| Resource Allocation | Oversees the allocation of resources and investment projects. |
| Economic Adjustment | Responsible for adjusting the economic structure and managing economic operations. |
| Sustainable Development | Promotes sustainable development and environmental protection. |
| Investment Promotion | Encourages both foreign and domestic investments. |
| Pricing Authority | Has significant influence over pricing regulations in various sectors. |
| International Cooperation | Engages in international economic cooperation and exchanges. |
| Data Collection | Collects and analyzes economic data for policy-making. |
The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) plays a crucial role in China's economic planning. One major initiative is the "13th Five-Year Plan," which focuses on innovation and sustainable development. It emphasizes enhancing technological capabilities to drive economic growth. Reports indicate that in recent years, R&D spending increased by over 10% annually, but some sectors still lag in innovation.
Another significant policy is related to energy efficiency. The NDRC aims to reduce energy consumption per unit of GDP by 15% by 2020. Despite strides in renewable energy, coal still dominates energy sources. Data shows coal-fired power contributes to over 50% of energy consumption. This reliance raises questions about environmental sustainability.
Additionally, the NDRC has introduced reforms in pricing policies. The goal is to make energy prices more reflective of market conditions. While this should foster competition, it can lead to rising costs for consumers. Reports indicate that public resistance to price hikes remains a challenge. Balancing these interests is an ongoing struggle for the commission.
The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) has been instrumental in shaping China's economic policies. The following bar chart illustrates the major initiatives and policies that have significantly impacted national development.
The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) plays a critical role in shaping China's economic landscape. This agency formulates policies that guide the nation’s development. It impacts investment decisions, infrastructure projects, and energy strategies. For instance, NDRC's plans often prioritize sustainable development. This focus can drive innovation in green technologies, pushing China towards a more eco-friendly future.
However, not all initiatives have been successful. Sometimes, ambitious projects face implementation challenges. Delays in approvals or funding can hinder progress. For example, infrastructure plans may not align perfectly with local needs, resulting in unused facilities. Balancing national goals with regional realities is tricky. The NDRC continuously seeks ways to refine its strategies, learning from past mistakes.
Moreover, public feedback is essential in this process. Engaging local communities can enhance project relevance. When the voices of citizens are heard, projects often succeed more. The NDRC must remain adaptable, addressing both successes and failures. This is vital for sustainable growth in China's ever-evolving economy.






