Industrial Water Treatment Plants (WTP) play a crucial role in addressing the ever-growing demand for clean and sustainable water management in various industries. As industrial processes often consume large quantities of water and generate significant amounts of wastewater, the adoption of advanced water treatment solutions is essential to meet environmental regulations and ensure operational efficiency. An effective Industrial WTP not only purifies water for reuse, but also minimizes the ecological footprint of industrial activities.
The benefits of Industrial WTP extend beyond mere compliance; they contribute to economic savings, resource conservation, and enhanced productivity. By implementing sophisticated treatments, industries can reduce their dependency on municipal water supplies and lower treatment costs for their wastewater, transforming a potential liability into a valuable resource. In an era where sustainability is paramount, understanding how Industrial WTP functions and its advantages can empower industries to make informed decisions that align with both their operational goals and environmental responsibilities.
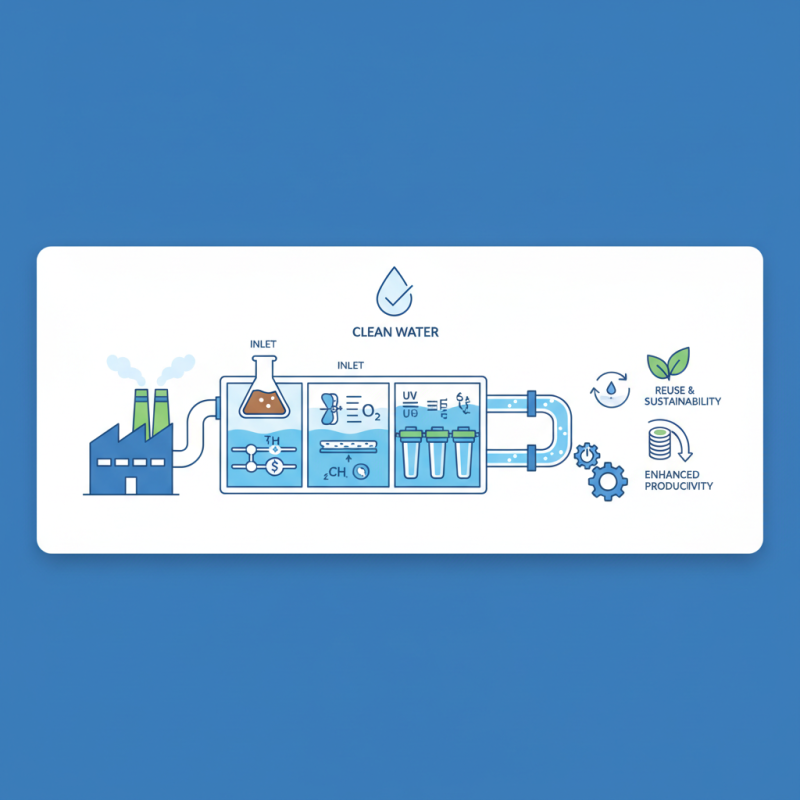
Industrial Water Treatment Plants (WTPs) play a crucial role in managing water resources in various industries. These facilities are designed to treat and purify water used in industrial processes, ensuring that the water meets specific quality standards for operational efficiency and environmental compliance. This treatment typically involves a series of processes including filtration, chemical treatment, and disinfection, catering to the unique needs of different industrial applications.
The operation of an Industrial WTP is essential for minimizing the environmental impact of industrial activities. By effectively removing contaminants and pollutants from water, these plants facilitate the safe discharge of treated water back into natural water bodies or allow for its reuse within the industry. Furthermore, WTPs help industries conserve freshwater resources, reduce operational costs associated with water procurement and waste management, and promote sustainable practices that align with regulatory requirements.
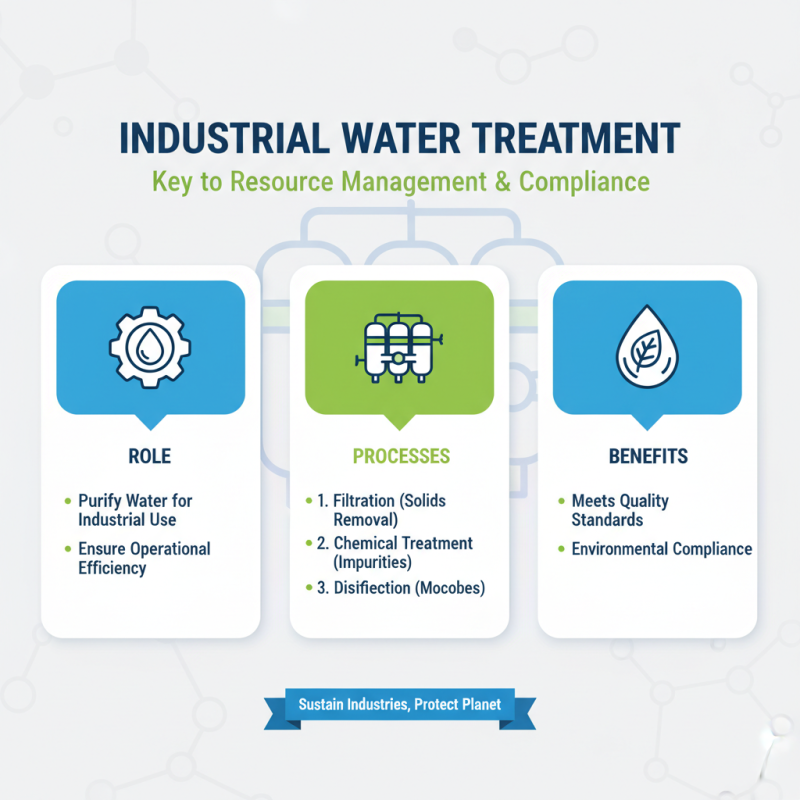
Industrial Water Treatment Processes (WTP) play a pivotal role in managing water resources effectively. The key components include filtration systems, chemical dosing systems, sedimentation tanks, and disinfection units.
Filtration systems are essential for removing particulate matter from water, enhancing the clarity and overall quality. Chemical dosing systems introduce necessary chemicals to adjust water chemistry, neutralize contaminants, or aid in the flocculation process, which is crucial for subsequent treatments.
Sedimentation tanks provide a space for heavier particles to settle out of the water, significantly improving the efficiency of the treatment process. Following this step, disinfection units utilize methods such as UV light or chlorine to eliminate harmful microorganisms, ensuring the treated water is safe for use in various industrial applications.
Tip: Regular maintenance of your filtration and disinfection systems is crucial to ensure optimal performance and prolong the lifespan of the equipment. Monitoring water quality parameters can help in adjusting the treatment processes proactively.
Additionally, the integration of advanced monitoring technologies, such as sensors and automation systems, improves the precision of water treatment processes. This not only increases efficiency but also allows for real-time adjustments to maximize water quality.
Tip: Investing in training for personnel involved in water treatment can greatly improve operational efficiency and safety, ensuring that the latest technologies and methods are effectively utilized.
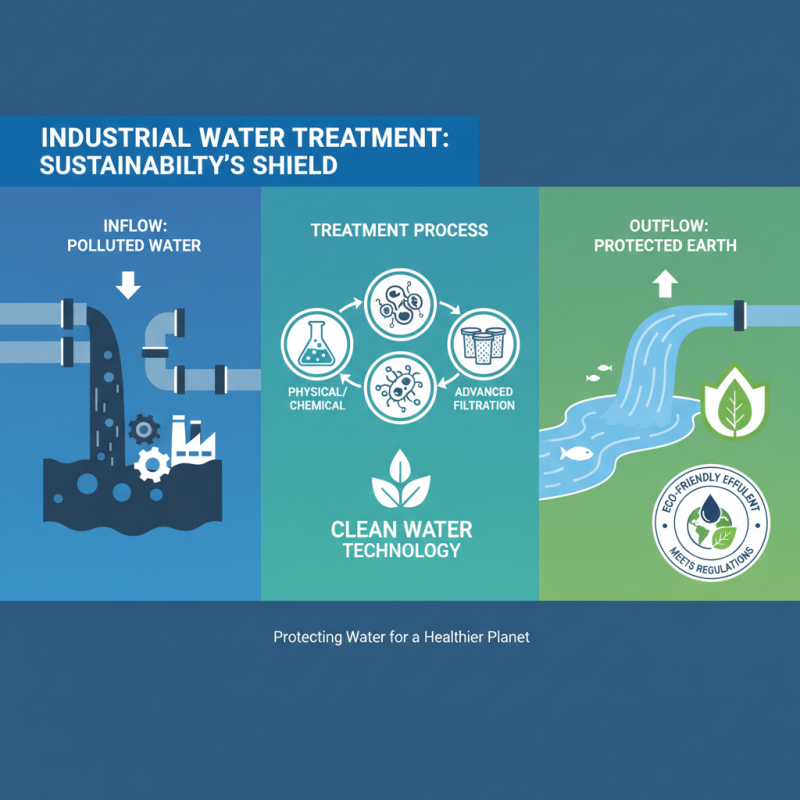
Industrial Water Treatment Plants (WTPs) play a crucial role in promoting environmental sustainability by effectively managing and treating industrial wastewater. These facilities employ advanced technologies to remove contaminants and reduce pollutants before they are discharged into natural water bodies. By ensuring that the effluents meet regulatory standards, industrial WTPs help protect aquatic ecosystems and preserve water quality, which is vital for both human health and biodiversity.
Moreover, the implementation of industrial water treatment processes significantly contributes to resource conservation. By treating and recycling wastewater, industries can reduce their reliance on freshwater sources, minimizing the strain on local water supplies. This practice not only helps in conserving water resources but also reduces the overall environmental impact associated with water extraction and use. The adoption of sustainable water management strategies in industrial operations ultimately fosters a healthier environment and supports the global goals of sustainability and climate resilience.
In the realm of industrial water treatment, technological innovations are playing a transformative role. With increasing regulatory demands and the pressing need for sustainable practices, industries are turning to advanced technologies to enhance their water treatment processes. According to a report by the International Water Association, the global industrial wastewater treatment market is expected to grow to $XXX billion by 2025, driven largely by the need for efficient water management strategies.
One of the most significant advancements in this field is the integration of smart technologies, such as IoT devices and AI-driven analytics. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring of water quality and treatment efficiency, enabling companies to optimize their processes and reduce operational costs. For instance, data from the Water Research Foundation indicates that facilities adopting smart technologies can achieve up to a 30% reduction in energy consumption and chemical usage. This not only improves the overall environmental impact but also enhances compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Tips: When considering technological upgrades, industries should focus on scalability and adaptability. Investing in modular treatment systems can provide flexibility to meet future needs without significant capital expenditures. Additionally, continuous training for staff on new technologies ensures that the benefits of innovation are fully realized, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency. Embracing these innovations positions companies not just to comply but to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.
This chart illustrates the effectiveness of various industrial water treatment technologies in reducing contaminants. The data shows the percentage reduction of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD), and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) by different treatment methods.
Industrial Water Treatment Plants (WTP) are designed to optimize the recycling and reuse of water in various industrial processes. However, they face significant challenges that can hinder their efficiency and effectiveness. One of the primary challenges is the variability in feed water quality. According to a report from the Water Environment Federation, variations in water composition can lead to inconsistent treatment outcomes, which not only affects operational performance but also increases costs. Industries often encounter issues such as high turbidity levels or fluctuations in chemical composition that require adaptive treatment strategies.
To address these challenges, various solutions have emerged. The implementation of advanced filtration and purification technologies, such as membrane technologies, has proven effective in managing quality variations. A study published in the Journal of Water Process Engineering highlighted that integrating modular treatment systems allows for scalability and flexibility, enabling industrial WTPs to adjust to new water quality parameters easily.
Additionally, real-time monitoring and data analytics are shaping a new era of proactive management in water treatment operations, allowing facilities to predict and respond to changing conditions more efficiently. Emphasizing the need for continuous innovation, the global water treatment market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2021 to 2028, highlighting the urgency for industries to adopt state-of-the-art solutions to overcome these operational hurdles.






