Industrial Recycling plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing and waste management. According to Dr. Jane Smith, an expert in recycling technologies, "Industrial Recycling not only conserves resources but also fuels innovation." This highlights the dual benefit of recycling within the industry.
Recycling materials like metals and plastics reduces the need for virgin resources. Factories can repurpose waste instead of sending it to landfills. However, many industries still overlook this vital process. The complexity of recycling systems can deter companies from implementing effective practices.
Despite existing programs, there is room for improvement. Many businesses have yet to integrate sustainable practices fully. Industrial Recycling requires collaboration among manufacturers, policymakers, and the community. Only then can we realize its true potential for a cleaner environment and a sustainable future.

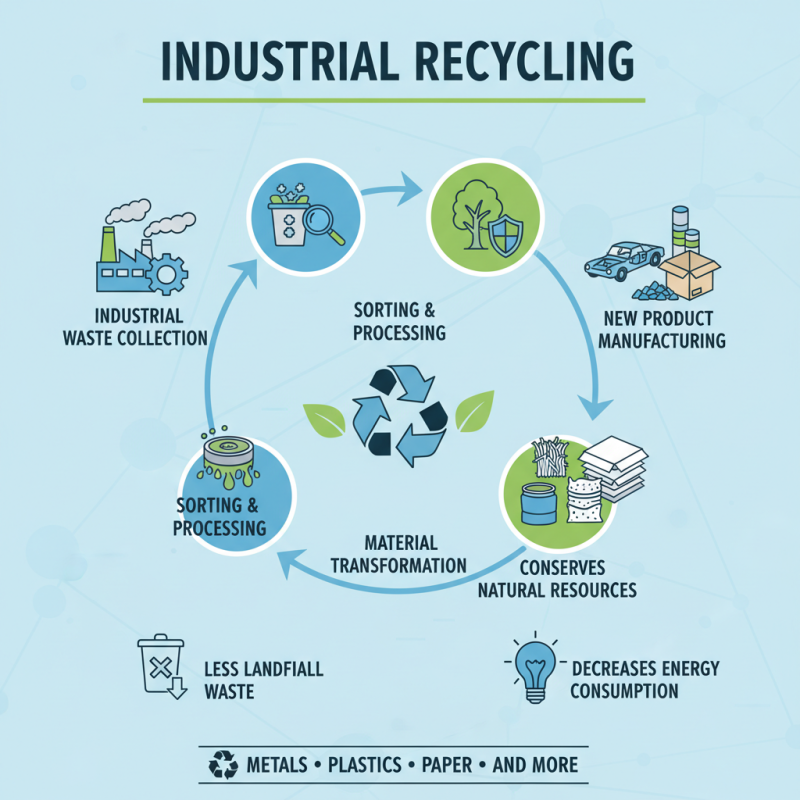
Industrial recycling is a process that repurposes waste materials from various industries. This process helps reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. It also conserves natural resources and decreases energy consumption. Through recycling, materials like metals, plastics, and paper are collected and processed. They are then transformed into new products.
The process starts with sorting and collecting industrial waste. This can be a messy job. Often, companies overlook small scraps that can be recycled. Once sorted, materials undergo several treatment steps. This includes shredding, cleaning, and melting in some cases. Each step is crucial. However, mistakes can happen. Not all items are captured during the initial sorting.
Understanding industrial recycling is important. It addresses environmental issues and promotes sustainability. Yet, there is room for improvement. Not every company has a perfect system in place. Some may not recycle efficiently due to lack of awareness. Efforts should be made to educate employees. Additionally, better technology can enhance recycling processes.

Industrial recycling plays a crucial role in sustainability. It encompasses the recycling of various materials, primarily metals and plastics. These materials are not only abundant but also vital to numerous industries.
Metals are central to industrial recycling. According to a report by the Aluminum Association, recycling aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum. This recycling process effectively reduces greenhouse gas emissions and conserves natural resources. In 2020, about 75% of the aluminum produced in the U.S. came from recycled sources. However, despite this success, challenges remain. Many metals still go unrecycled. For instance, steel recycling rates vary widely across regions.
Plastics present a different challenge. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) noted that only about 9% of plastic waste is recycled in the U.S. This low rate highlights a significant gap. Many industries struggle to find ways to effectively recycle complex plastic products. The lack of standardization in plastic materials complicates recycling efforts. As a result, tons of plastics end up in landfills or oceans, causing environmental harm.
Understanding these key materials is vital for improving recycling processes. While industries have made strides, there’s much work to be done. Enhanced collaboration and innovation are needed to boost recycling rates across all sectors. We must reflect on our current practices and seek better solutions.
Industrial recycling has become a crucial aspect of economic sustainability. According to a report by the Recycling Partnership, recycling and reuse activities contribute nearly $5.5 billion to the U.S. economy. This figure is not just a number; it represents real savings and job opportunities for communities. Companies adopting recycling practices often see significant cost reductions in waste disposal. By reusing materials, businesses can lower their raw material costs, leading to better profit margins.
Job creation is another vital benefit. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that for every job in recycling, there are about 1.17 jobs created in the recycling processing and manufacturing sectors. This means that promoting recycling in industries not only helps in waste management but also provides meaningful employment. Local economies gain strength when these jobs are filled, creating more vibrant communities.
Tips: Evaluate your company's waste streams. Identify materials that could be recycled. Engage with local recycling facilities. Another tip is to train employees about the importance of recycling. Small steps can lead to big economic changes. Every effort counts in building a sustainable future.
Industrial recycling plays a crucial role in reducing waste and minimizing emissions. It involves processing materials that are discarded during manufacturing. This not only conserves resources but also diminishes the need for new raw materials. For example, recycling metals can save significant energy compared to extracting virgin materials. By focusing on these processes, industries can lessen their environmental footprint.
The benefits are evident, yet challenges remain. Many companies struggle with efficient recycling methods. Sometimes, materials are contaminated or improperly sorted. This leads to increased waste instead of reducing it. Not all industries have the same approach, and some lag behind. Progress is uneven, which can hinder overall effectiveness. Understanding this gap is essential for improvement.
Moreover, the emissions reductions achieved through recycling aren't always straightforward. Some processes can generate pollutants, potentially offsetting gains. Efforts must be directed to innovate and utilize cleaner technologies. Continuous evaluation and adaptation are necessary to truly champion industrial recycling. While the commitment to recycle is growing, the journey toward sustainability is ongoing. This requires critical thinking and collective responsibility.
| Recycling Material | Recycling Rate (%) | Reduction in Landfill (tons) | CO2 Emissions Reduced (tons/year) | Energy Savings (MWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardboard | 85 | 200,000 | 150,000 | 100,000 |
| Metals | 90 | 300,000 | 200,000 | 150,000 |
| Plastics | 25 | 50,000 | 30,000 | 20,000 |
| Glass | 70 | 100,000 | 80,000 | 60,000 |
| Electronics | 15 | 10,000 | 5,000 | 3,000 |
Industrial recycling plays a vital role in sustainability. However, challenges persist in this sector. Many facilities struggle to efficiently process materials. Outdated technologies can slow down operations. The lack of standardization adds complexity. Each facility may have different requirements, which complicates recycling efforts.
Innovations are emerging to address these issues. Advanced sorting technologies can improve material recovery rates. Artificial intelligence is being used to identify and separate recyclables automatically. These methods promise greater efficiency. Yet, the implementation can be costly and requires training.
The workforce faces hurdles too. Workers need to adapt to new systems. This can lead to resistance and error. Establishing a culture that embraces change is crucial. Without it, progress may stall. The industrial recycling sector must continually reflect on these challenges. Addressing them head-on can lead to a more sustainable future.